Spectravideo X'press (SVI-738)
It's an MSX-compatible (MSX version 1, but with some
extensions from v.2) computer, popular in Polish schools. There wasn't
much Polish software for it, as it was probably only MSX known in Poland.
Floppy disk drive and BASIC ASCII capabilities made this computer good
in data processing, but floppy disk drive was noisy (despite all rubber
pads and springs) and formatted only one side of 3.5-inch disk. Finally,
it was mostly used to teach BASIC programming.
It was called X'press, as it was relatively small and was offered with
bag for easy transporting.
In fact, Spectravideo X'Press is more MSX 2 than 1. It seems that
engineers planned to do something better, but costs didn't let them put
it to production. First mainboards had ready pads for battery-backed RTC,
one of MSX 2 standard requirements.
In fact, to convert it to MSX2 (except this clock), you have only to add
more VRAM, change ROMs, get the missing ROM address line and ground one
line in RS232 ROM driving circuit.
More, putting AC transformer in external case, but leaving switching
regulator with hot Gretz bridge in the computer seems to be
quick-and-dirty solution to interference problems.
| Manufacturer | Spectravideo | |
| Origin | Hong Kong | |
| Year of unit | 1987 | |
| Year of introduction | 1986 | |
| End of production | ?1988? | |
| CPU | Z80 | |
| Speed | 3.5MHz | |
| RAM | 64K | |
| ROM | 56K (32K BASIC, 8K serial, 16K FDC) | |
| Colors: | 256 | |
| Sound: | 3-channel AY-3-8910 | |
| OS: | MSX BASIC, MSX DOS CP/M 2.2 |
|
| Display modes: | Text: 40x24, 32x24,
80x24 Graphic: 256x192, 64x48. |
|
| Media: |
Tape ROM Cartridge Built-in floppy disk drive |
|
|
Power supply: |
||
|
A female DC Jack at the computer:
DC can be used in any polarity, but avoid it, as diodes may get hot after extensive use. |
||
| I/O: | 2x Joystick Tape Serial port (RS232) External FDD, Printer (merely Centronics compatible) Composite video Audio RF out |
|
| Possible upgrades: | To +/- MSX2 standard | |
| Software accessibility: | Quite easy (dedicated MSX sites) | Dedicated accessories in collection: |
My unit comes from school, so it had all damages it could get in school. FDD had to be replaced, as head was damaged by sticking pencil in there. I don't know if cartridge slot works, as I spent over hour with pliers making pins straight in their places. Cartridge door's hinge was broken on casing's side, fortunately it's easy to fix by glueing piece of round plastic inside (in my case plastic piece of wall screw plug cut to fit and act as hinge).
My unit, sold by Składnica Harcerska, is converted to support diacritized Polish characters: It has modified keys to show these characters on keys and modified ROM, to get them on screen with CODE/GRAPH keys.
| Contents: | Starting | Recording media | Pinouts | Links |
Starting:
It boots to MSX BASIC, where you can use commands native
to MSX BASIC:
MOTOR ON or MOTOR OFF - turns cassette motor on and off, usable when
motor driving connector is connected to cassette player.
CLOAD - loads MSX BASIC file from cassette. You use: CLOAD "PROGRAMNAME"
or to load the first one - just CLOAD.
To verify program written with CSAVE "PROG1", you have to type CLOAD?"PROG1".
LOAD"CAS:PROGNAME" - or LOAD"CAS:" - loads ASCII file, may be also BASIC
program saved with SAVE"CAS:PROGNAME".
BLOAD"CAS:PROGNAME" or BLOAD"CAS:" - loads a machine code program (binary)
from cassette.
LOAD and BLOAD may have additional ,R parameter at the end (for example
BLOAD"CAS:",R). With this the program will be started immediately after
loading.
To load from disk, check first is diskette bootable by
trying to boot computer from it.
If not, use FILES command to list contents in BASIC.
Now, you can:
RUN"[1:]PROGNAME" - loads and runs program from disk. Some MSX BASIC
versions have not 1: but A: drive letters.
LOAD"[1:]PROGNAME" - Loads BASIC file.
BLOAD"[1:]PROGNAME" - Loads binary file.
If you put a CP/M or MSX-DOS disk to the computer and
start it, it'll bot into CP/M or MSX-DOS. CP/M commands are similar to
DOS.
Recording media
Recording disks from DSK requires PC with floppy
drive. Floppies usually must be formatted in Spectravideo before making,
so to format it, use
CALL FORMAT
command from BASIC on Your Spectravideo.
DSK files may be recorded with Disk Manager, but not all of them. Some requires DCOPY, making of DSK can be done with DCOPY too, but to make it working properly you have to run in in PURE DOS, NOT in Windows.
IMG files are usually CP/M files, and can be recorded
using COPYQM (available in my fileland with SVI-738 system disks) with
the following command:
COPYQM A: PLAYBACK=IMAGE.IMG
Tapes are usually stored as CAS files, they may be just played from sound card. Use CasTools to process CAS to WAV and in reverse way.
Pinouts:
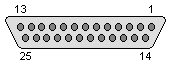
External floppy disk drive:
|
|
|
| 1 - +12V 2 - +5V 3 - +5V 4 - /INDEX 5 - /DSEL1 6 - DIRECTION 7 - /STEP 8 - WRITE DATA 9 - /WRITE GATE 10 - /TRACK0 11 - /WRITE PROT. 12 - READ DATA 13 - /SIDE SEL |
14 - +12V 15 - +12V 16 - +5V 17 - /DSEL0 18 - MOTOR ON 19 - READY 20 - GND 21 - GND 22 - GND 23 - GND 24 - GND 25 - GND |
You can use normal PC drive, but if you plan to use PC FDD as internal one, be sure to select it as drive 0 - DS0, not DS1 as it was in PC. Older drives have jumpers to set it. Newer - solder pads. Successfully used Alps drive only by modifying its solder pads.
Tape connector:
|
|
| 1-3 - GND 4 - DATA OUT 5 - DATA IN 6 - RELAY 7 - RELAY 8 - GND |
Computer controls relay - to start/stop tape, pins 6 and 7 are connected together when tape must be running.
Printer connector - 14-pin female Centronics-type connector:
|
|
|
| 1 - /STB 2 - PD0 3 - PD1 4 - PD2 5 - PD3 6 - PD4 7 - PD5 |
8 - PD6 9 - PD7 10 - NC 11 - BUSY 12 - NC 13 - NC 14 - GND |
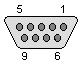
RS232 connector (not sure about it!):
|
|
| 1 - GND 2 - TxD 3 - RxD 4 - RtS 5 - CtS 6 - DSR 7 - GND 8 - CD 9 - DTR |
In many cases you can use this port to exchange programs - just
use COM0 device, for example:
LOAD"COM0:"
Links:
http://www.faq.msxnet.org/ - MSX FAQ - Everything you want to know.
http://msx.hansotten.com/ -
Many useful docs, for example converting SVI-738 to MSX2.
http://www.bluemsx.com/ - Emulator
and games database, some with download.
http://web.archive.org/web/20040610094214/http://svi.s31.pl/ - in
English, site ran by Polish collector, many interesting facts about SVI.
http://www.msxarchive.nl/
- Lots of downloadable software
http://msx.fi/nyyrikki/pc.html
- Some software.
http://fms.komkon.org/MSX/
- Some nice resources from MSX fans Usenet.
http://web.archive.org/web/20141020055241/http://www.spectravideo.org/manuals.html
- Manuals, screenshots and projects for SVI. Downloads GONE.
http://www.samdal.com/spectravideo.htm - Resources, schematic of
SVI-738.